Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
土屋 晴文; 榎戸 輝揚*; 和田 有希*; 古田 禄大; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 楳本 大悟*; 牧島 一夫*; GROWTH Collaboration*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 358, p.1163_1 - 1163_6, 2021/07
Since 2006, the GROWTH experiment has been successfully operating at the coastal area of Japan Sea. The GROWTH experiment aims at elucidating how particles in lightning and thunderclouds are accelerated to relativistic energies to produce gamma rays and occasionally neutrons. According to observations done by the GROWTH experiment, it is found that there are two types of radiation bursts associated with winter thunderstorms. One is long bursts lasting for a few tens of seconds to a few minutes, being not clearly related to lightning. The other is short bursts in association with lightning. To better understand the production mechanism of these radiation bursts, we have developed a small-type of radiation detectors and increased observational points with the new detectors. In this presentation, we show an overview of observations done by the GROWTH experiment. Then we focus on recent several findings observed by the new detectors. One, which is categorized into long bursts, implies a relationship between a long burst and an intra/inter-cloud discharge. Another is a combination of short bursts and long ones, showing simultaneous detections of prompt gamma rays extending up to 10 MeV and the 511-keV annihilation ones. These gamma-ray signals demonstrate the occurrence of photonuclear reactions in lightning. Based on these results, we discuss the production mechanism of gamma rays related to thunderstorms.
榎戸 輝揚*; 和田 有希*; 土屋 晴文
日本物理学会誌, 74(4), p.192 - 200, 2019/04
近年、日本海沿岸にある原子力発電所や自治体がもつ放射線モニタリングポストにより、冬に発生する雷や雷雲の接近に伴い、高エネルギーの放射線の増大が観測されていた。この増大の正体を明かすために、日本海沿岸に位置する柏崎刈羽原子力発電所構内に新型の検出器を設置し、2006年から観測を実施している。また2015年には安価で小型な観測装置を開発し、金沢市や小松市などにも観測拠点を構築してきた。そうした10年以上にわたる観測の結果、雷や雷雲が電子を相対論的なエネルギーに加速できる天然の粒子加速器であることを観測的に実証するとともに、雷が光核反応を引き起こし、中性子や陽電子の発生にも寄与しているという驚くべき事実も明らかにしてきた。こうした放射線観測は、従来の光や電波観測からだけではわからなかった、雷や雷雲が高エネルギー物理現象の現場であるという側面を浮かび上がらせた。本稿では、我々が得た観測結果を解説するとともに、古典的な可視光から電波の観測のみならず、X線や 線の観測、宇宙線,原子核物理や大気化学に広がる「雷雲や雷の高エネルギー大気物理学」という新しい学際分野を紹介する。
線の観測、宇宙線,原子核物理や大気化学に広がる「雷雲や雷の高エネルギー大気物理学」という新しい学際分野を紹介する。
和田 有希*; Bowers, G. S.*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 鴨川 仁*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; Smith, D.*; 古田 禄大*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 45(11), p.5700 - 5707, 2018/06
被引用回数:30 パーセンタイル:81.28(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)An on-ground observation program for high energy atmospheric phenomena in winter thunderstorms along Japan Sea has been performed via lightning measurements of  -ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded
-ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded  -ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The
-ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The  -ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36
-ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36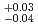 , being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a
, being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a  -ray glow). Then the
-ray glow). Then the  -ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed
-ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed  50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over
50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over  60km area with a
60km area with a  300 ms duration. The timing of the
300 ms duration. The timing of the  -ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the
-ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the  -ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
-ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
 -ray observations at the coastal area of Japan sea
-ray observations at the coastal area of Japan sea土屋 晴文
no journal, ,
Since 2006, the Gamma Ray Observation of Winter Thundercloud (GROWTH) experiment has been successfully operating at the coastal area of Japan sea. The GROWTH experiment aims at elucidating how particles in lightning and thunderclouds are accelerated to relativistic energies to produce  rays and occasionally neutrons. According to observations done by the GROWTH experiment, it is found that there are two types of radiation bursts associated with thunderstorm activities. One is long bursts lasting for a few tens of seconds to a few minutes, being not clearly related to lightning. The other is short bursts in association with lightning. In this presentation we explain general properties of the two sorts of bursts and then show two new findings recently observed. One, which is categorized into long bursts, clearly exhibits a relationship between a long burst and an intra/inter-cloud discharge. The other is a combination of short bursts and long ones, providing a new insight into the nature of short bursts, with simultaneous detections of prompt
rays and occasionally neutrons. According to observations done by the GROWTH experiment, it is found that there are two types of radiation bursts associated with thunderstorm activities. One is long bursts lasting for a few tens of seconds to a few minutes, being not clearly related to lightning. The other is short bursts in association with lightning. In this presentation we explain general properties of the two sorts of bursts and then show two new findings recently observed. One, which is categorized into long bursts, clearly exhibits a relationship between a long burst and an intra/inter-cloud discharge. The other is a combination of short bursts and long ones, providing a new insight into the nature of short bursts, with simultaneous detections of prompt  rays and the annihilation ones. These
rays and the annihilation ones. These  -ray signals enabled us to confirm that photonuclear reactions certainly take place in a lightning discharge.
-ray signals enabled us to confirm that photonuclear reactions certainly take place in a lightning discharge.